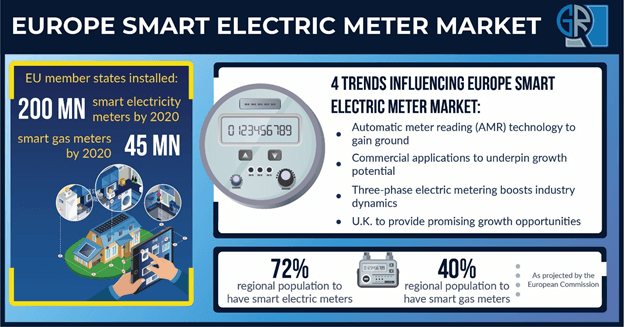
Powered by ongoing digitalization, electrification, and decentralization efforts across the region, Europe smart electric meter market is riding on a high growth wave. Considering the ever-growing power demand and addition of new energy sources, smart meters are critical for the electricity sector and are seen as the foundation required for the deployment of renewable energy sources.
Smart meters are a critical tool for European customers and utilities in today’s time, where energy prices are rising. Data from advanced metering may be utilized to give consumers advice on how to optimize their energy consumption and lower their bills. This is the goal of a new smart meter-enabled gadget announced in late October 2021, by Samsung. The technology, Samsung SmartThings Energy, allows users to use their smart meter data with the tool for remotely regulating the energy usage of their domestic home appliances from anywhere, for free.
Smart electric meters for commercial applications
There has been an increase in product demand as energy-efficient and low-maintenance equipment offer greater profits in billing of data centers, as well as public and private offices. Smart metering technologies enable utility firms to monitor demand and supply networks and respond to current events more efficiently.
The data may be gathered even from meters that are difficult to reach or are positioned at great distances apart. They are provided on a regular basis, notifying the end-user of the reading, transmission data, and any problems and mistakes. This allows teams to be dispatched relatively instantaneously to wherever they are needed at any given time.
All of this is done in order to respond as promptly as possible if an issue emerges, ensuring optimal productivity alongside minimal downtimes. One of the significant factors favoring product deployment is the growing customer inclination towards adopting sustainable technologies to manage and monitor power use.
Investments in smart home appliances across the Netherlands
The Netherlands appears to be ahead of all the member states in the EU in terms of smart device adoption. While 69% of individuals between age 16 and 74 owned smart devices during 2020, the overall EU average stood at a mere 8%., clearly indicating the leading position of the Dutch smart electric meters market.
According to this recent survey conducted by Statistics Netherlands from April to July 2020, about 72% of the Dutch population aged 12 and above owned at least one device connected to the Internet of Things (IoT). Nearly 59% of the participants stated that they had installed a smart electricity, gas, or water meter at their home.
The nation is also a frontrunner in the adoption of virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Home, as well as smart watches, smart refrigerators, and smart lighting. It was revealed that among the 6.5 thousand participants, smart meters for electricity, gas, and water were especially popular.
Germans inclined to save more on energy bills
Many European countries are investing in smart metering in order to reach the European Union's energy objectives by 2020. Speaking of Germany, smart energy grid networks are being developed and used in a variety of industries to improve the efficiency of power supply and consumption across the region.
The country's construction sector is receiving huge investments from both public and private sector enterprises, in order to expand the number of building projects. Remote places, such as villages, are seeing an increase in electrification operations as various power production corporations establish facilities in these areas.
Many off-grid communities are being incorporated into the main power grid infrastructure. E. ON, a European electric utility company, deployed approximately 20,000 smart meters in Germany in 2020. These meters are providing clients with detailed and graphical energy information.


